Introduction to Rivers in Hindi
Rivers, known as **नदियाँ** in Hindi, are one of the most vital natural resources on our planet. They play an essential role not only in the ecosystem but also in the cultural, historical, and economic aspects of human life. In India, the significance of rivers is deeply ingrained in religious beliefs, folklore, and daily living. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of rivers in Hindi, including their importance, major rivers in India, and their impact on society.
Importance of Rivers
The **नदियाँ** are often referred to as the lifelines of the areas they flow through. They provide water for drinking, irrigation, and industry. Agriculture, which is a cornerstone of the Indian economy, heavily relies on rivers. The fertile plains adjacent to rivers facilitate the growth of crops, making them essential for food production.
Additionally, rivers contribute to the overall biodiversity of the regions they traverse. They serve as habitats for numerous species of flora and fauna and support various ecosystems. Many communities rely on rivers for their livelihoods, including fishing and tourism.
Major Rivers in India
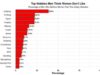
India boasts some of the most significant and revered **नदियाँ** in the world. Here are a few of the major rivers:
- Ganga (गंगा): The Ganges is not only one of the longest rivers in India but also one of the most sacred. It flows through northern India and is worshipped by millions. The Ganga is pivotal for agriculture, drinking water, and supporting a diverse ecosystem.
- Yamuna (यमुना): A major tributary of the Ganges, the Yamuna flows through several states, including Delhi. Its banks are home to significant cultural heritage sites, making it essential to India’s history.
- Brahmaputra (ब्रह्मपुत्र): Originating in Tibet, the Brahmaputra traverses through northeastern India. It is known for its massive size and is crucial for the economy of the region, providing irrigation and supporting fishing industries.
- Godavari (Godavari): The Godavari is the second-longest river in India, flowing through the states of Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Odisha. Its basin is known for rich agriculture.
- Krishna (कृष्णा): Another major river, the Krishna, flows across the states of Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh, contributing significantly to their agricultural sectors.
Cultural Significance of Rivers
The **नदियाँ** hold immense cultural and spiritual significance in India. Many religious rituals and festivals are conducted on the banks of these rivers. The Ganges, for instance, is believed to cleanse sins and is a prominent site for followers of Hinduism. Pilgrimages to rivers for rituals such as the ‘Ganga Snan’ (bathing in the Ganga) are common practices among devotees.
Moreover, rivers are often personified in various mythologies and epics, giving them a divine identity. The character of rivers in Indian literature and art reflects their centrality in the societal consciousness.
Environmental Challenges
Efforts to clean and restore rivers have gained momentum, with initiatives like the «Namami Gange» project aimed at rejuvenating the Ganga. Such programs emphasize the need for sustainable practices to protect these vital resources.
Conclusion
The **नदियाँ** are much more than mere water bodies; they are the lifeblood of civilization, woven into the social, economic, and spiritual fabric of Indian life. Their significance cannot be overstated, as they have shaped landscapes, cultures, and civilizations for centuries. Protecting and preserving rivers is crucial for maintaining ecological balance, ensuring water security, and upholding cultural heritage. It is essential for current and future generations to be conscious of the importance of rivers and work towards their conservation.
In understanding the importance of rivers in Hindi, we not only recognize their physical presence but also celebrate their role in nurturing life, culture, and the environment.